MySql:多表查询
多表关系
- 一对多
- 一对一
- 多对多
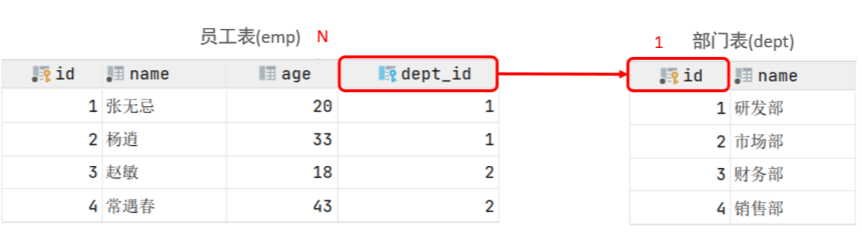
一对多
案例: 部门 与 员工的关系
关系: 一个部门对应多个员工,一个员工对应一个部门
实现: 在多的一方建立外键,指向一的一方的主键
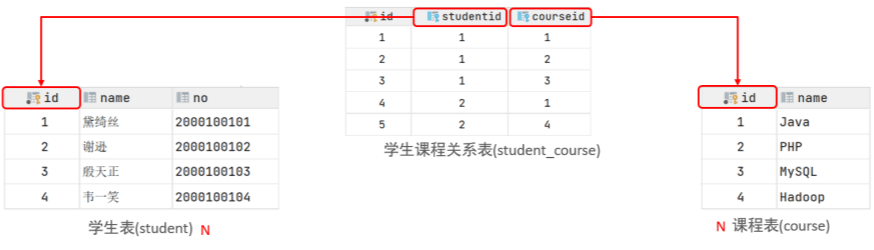
多对多
案例: 学生 与 课程的关系
关系: 一个学生可以选修多门课程,一门课程也可以供多个学生选择
实现: 建立第三张中间表,中间表至少包含两个外键,分别关联两方主键
一对一
案例: 用户 与 用户详情的关系
关系: 一对一关系,多用于单表拆分,将一张表的基础字段放在一张表中,其他详情字段放在另一张表中,以提升操作效率
实现: 在任意一方加入外键,关联另外一方的主键,并且设置外键为唯一的(UNIQUE)
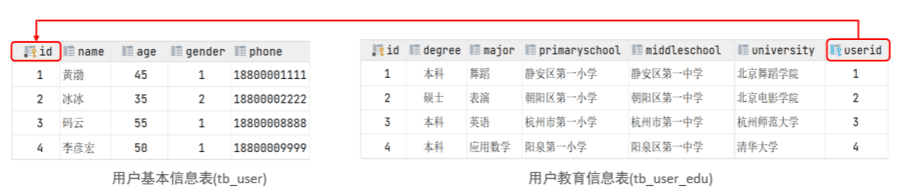
内连接
内连接的查询语法:
隐式内连接:select 字段列表 from 表1,表2 where 条件....;
显示内连接:select 字段列表 from 表1 [inner] join 表2 on 链接条件....;
如上面一对多的数据表,查询员工姓名以及对于的部门:
select emp.name , dept.name from emp,dept where emp.dept_id=dept.id;
select e.name , d.name from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
外连接
左外连接:select 字段列表 from 表1 left [outer] join 表2 on 条件 ... ;
相当于查询表1(左表)的所有数据包含表1表2 交集部分的数据.
右外连接:select 字段列表 from 表1 right [outer] join 表2 on 条件 ... ;
相当于查询表2(右表)的所有数据包含表1表2 交集部分的数据.
自连接
语法:select 字段列表 from 表A 别名A join 表A 别名b on 条件...;
自连接查询,可以是内连接查询,也可以是外连接查询
案例:
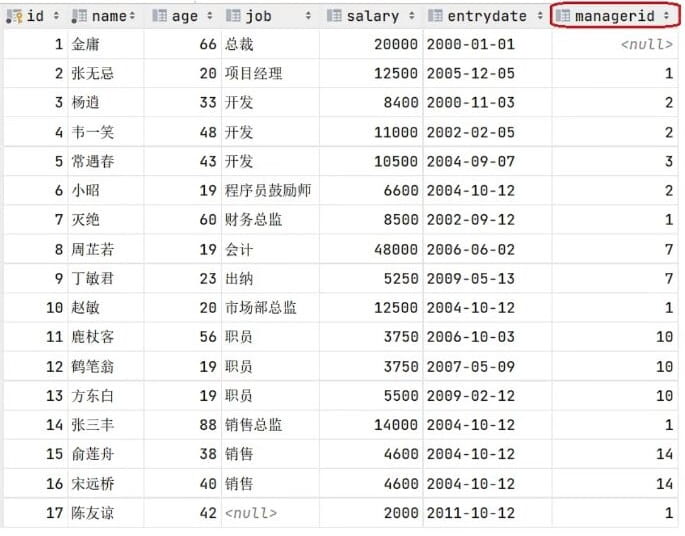
1.查询员工以及所属领导的名字(每条数据中的managerid对于其领导的id,自连接查询要将这个表看成是两个表进行查询)
select e1.name,e2.name from emp e1,emp e2 on e1.managerid=e2.id;(使用的内连接)
2.查询所有员工 emp 及其领导的名字 emp,如果员工没有领导,也需要查询出来.
select a.name '员工', b.name ’领导‘ from emp a left join emp b on where a.managerid=b.id;联合查询
对于联合查询来说,就是把多次查询的结果合并起来,形成一个新的查询结果集.
语法:
select 字段列表 from 表A ...
union [all]
select 字段列表 from 表B...;案例:
将薪资低于5000的员工,和年龄大于50岁的员工全部查询出来
select * from emp where salary < 5000
union all
select * from emp where age > 50;
--加上all,如果两个查询语句有重复的数据,联合起来会显示两次,去掉all,去重子查询
概念:SQL语句中嵌套select语句,成为嵌套查询,又称子查询
select * from t1 where column1=(select column1 from t2);子查询外部的语句可以是 insert/update/delete/select 的任何一个
根据子查询的结果不同,分为:
- 标量子查询(子查询结果为单个值)
- 列子查询(子查询结果为一列)
- 行子查询(子查询结果为一行)
- 表子查询(子查询结果为多行多列)
标量子查询
子查询返回的结果是单个值(数字,字符串,日期等),最简单的形式,这种子查询称为 标量子查询.
常用的操作符: = <> > >= < <=
查询在'东方白'入职之后的员工信息: select * from emp where entrydate > (select entrydate from emp where name = '东方白');
列子查询
子查询返回的结果是一列(可以是多行),这种子查询称为列子查询
常用的操作符:
- in(在指定集合范围内,多选一)
- not in(不在指定的集合范围之内)
- any (子查询返回的列表中,有任意一个满足即可)
- some(与any等同,使用some的地方都可以使用any)
- all (子查询返回列表的所有值都必须满足)
案例:
1.查询"销售部"和"市场部"的所有员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id in (select id from dept where name='销售部' or name = '市场部');2.查询 比 财务部 所有人工资 都高 的员工信息
select * from emp where gongzi>all(select gognzi from emp where dept_id=(select id from dept where name='财务部'));3.查询比研发部其中任意一人工资高的员工信息
select * from emp where gongzi>any(select gognzi from emp where id=(select id from dept where name='研发部'));行子查询
子查询返回的结果是一行(可以是多列),这种子查询为行子查询
常用的操作符:=,<>,in,not in
案例:
1.查询与"张无忌"的 薪资以及直属领导 相同的员工信息
select * from emp where (salary,managerid) = (select salary,managerid from emp where name='张无忌');表子查询
子查询返回的结果是多行多列,这种子查询称为 表子查询.
常用的操作符: in
案例:
1.查询与 鹿杖客 宋远桥 的职位和薪资相同的员工信息
select * from emp where (job,salary) in (select job,salary from emp where name='鹿杖客' or name=’宋远桥‘);2.查询入职日期是"2006-01-01"之后的员工信息,以及其部门的信息
select * from (select * from emp where entrydate>'2006-01-01') e left join dept d on e.dept_id=d.id;案例:
--查询员工的姓名,年龄,职位,部门信息(隐式内连接)
select e.name,e.age,e.job,d.name from emp e,dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;
--查询年龄小于30岁的员工的姓名,年龄,职位,部门信息(显示内连接)
select e.name,e.age,e.job,d.name from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age<30;
--查询拥有员工的部门ID,部门名称
select distinct d.id,d.name from emp e,dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;
--查询所有年龄大于40岁的员工, 及其归属的部门名称; 如果员工没有分配部门, 也需要展示出来(外连接)
select e.*,d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age>40;
--查询所有员工的工资等级 (工资等级有三个字段:等级grade,最低losal,最高hisal)
select e.* s.grade from emp e,salgrade s where e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal;
--查询研发部所有员工的信息以及 工资等级
select e.*,s.grade from emp e ,salgrade s ,dept d where e.dept_id=d.id and (e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal) and d.name = '研发部';
--查询‘研发部’员工的平均工资
select avg(e.salary) from emp e where e.dept_id=(select id from dept d where d.name='研发部');
--查询工资比“灭绝”高的员工信息
select * from emp e where where e.salary>(select e.salary from emp e where name='灭绝');
--查询比平均薪资高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary>(select avg(salary) from emp);
--查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息
select e1.* from emp e1 where e1.salary<(select avg(salary) from emp e2 where e1.dept_id=e2.dept_id );
--查询所有的部门信息,并统计部门的员工人数
select d.id,d.name,(select count(*) from emp e where e.dept_id=d.id) '人数' from dept d;
--查询所有学生的选课情况,展示出学生的名称,学号,课程名称
--表:student ,cource,student_course
--链接条件:student_id = student_course.studentid , course.id = student_course.courseid
select s.name,s.no,c.name from student s,student_course sc,course c where s.id=sc.studentid and sc.courseid = c.id;