大型商城:缓存 – SpringCache
springcache简介
每次都那样写缓存太麻烦了,spring从3.1开始定义了Cache、CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术。并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们的开发
SpringCache使用
1.引入依赖
spring-boot-starter-cache spring-boot-starter-data-redis
<!--springcache-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>2.写配置
- 自动配置了那些?
- CacheAutoConfiguration会导入 RedisCacheCinfiguration
- 自动配置号缓存管理器 RedisCacheManager
- 配置使用redis作为缓存
spring.cache.type=redis
3.测试使用
@Cacheable:触发将数据保存到缓存的操作
@CacheEvict:将数据从缓存中删除
@CachePut:不影响方法执行进行缓存更新
@Caching :组合以上多个操作
@CacheConfig:在类级别共享缓存的相同配置- 1.开启缓存功能 @EnableCaching
- 2.只需要使用注解就能完成缓存操作
//每一个需要缓存的数据都需要指定要放到哪个名字的缓存【缓存的分区,一般按照业务的类型来分】
//代表当前方法的结果需要缓存,如果缓存中有,方法不要调用,如果缓存中没,调用方法,再讲数据存入缓存
@Cacheable("category")
@Override
public List<CategoryEntity> getLevel1Categorys() {
List<CategoryEntity> categoryEntities = baseMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>().eq("cat_level", 1));
return categoryEntities;
}@Cacheable的细节设置
上面使用@Cacheable默认一下行为:
- 如果缓存存在,方法就不调用
- key默认生成,缓存的名字: :SimpleKey{ }
- 缓存的value值,默认使用jdk序列化机制,将序列化后的数据存到redis
- 默认ttl时间:-1 ,永不过期
自定义:
- 指定生成缓存使用的key:key属性指定
@Cacheable(value = "category",key="'level1Categorys'") - 指定缓存的数据存活时间 配置文件中:
spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=3600000 - 将数据保存为json格式 细说
将数据保存为json格式
新建一个配置类 MyCacheConfig
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class MyCacheConfig {
@Bean
public RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties) {
CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();
org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration config = org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
.defaultCacheConfig();
//指定缓存序列化方式为json
config = config.serializeValuesWith(
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
//设置配置文件中的各项配置,如过期时间
if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {
config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());
}
if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {
config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());
}
if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {
config = config.disableCachingNullValues();
}
if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {
config = config.disableKeyPrefix();
}
return config;
}
}
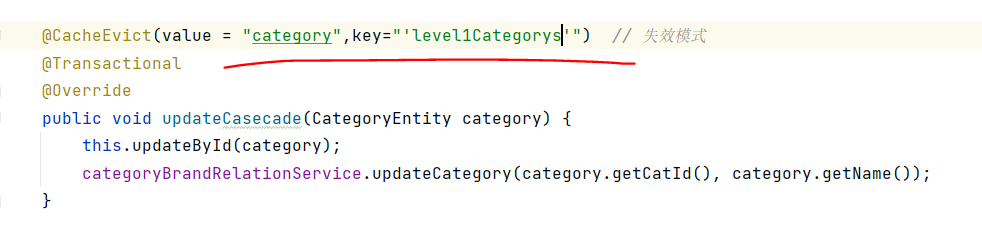
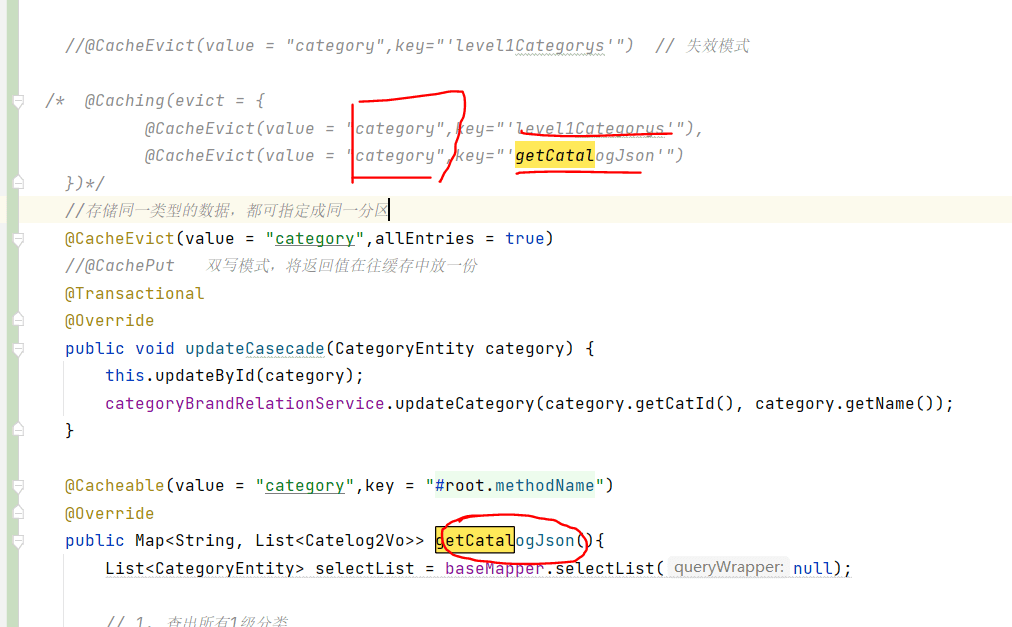
@CacheEvict
这是更新属性的方法,加上@CacheEvict,每当对属性进行修改,都会删除redis中缓存
最终:
springcache不足
1.读模式
- 缓存穿透:查询一个null数据.解决:缓存空数据:ache-null-values=true
- 缓存击穿:大量并发进来同时查询一个正好过期的数据,解决:加锁 ?
- 缓存雪崩:大量的key同时过期。 解决:加过期时间:spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=360000
2.写模式
- 读写加锁
- 引入canal,感知到mysql的更新去更新数据库
- 读多写多,直接去数据库查询
3.总结:
常规数据(读多写少,即时性,一致性要求不高的数据,完全可以使用Spring-Cache):
写模式(只要缓存的数据有过期时间就足够了)
特殊数据:特殊设计
阅读剩余
版权声明:
作者:Tin
链接:http://www.tinstu.com/2661.html
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END